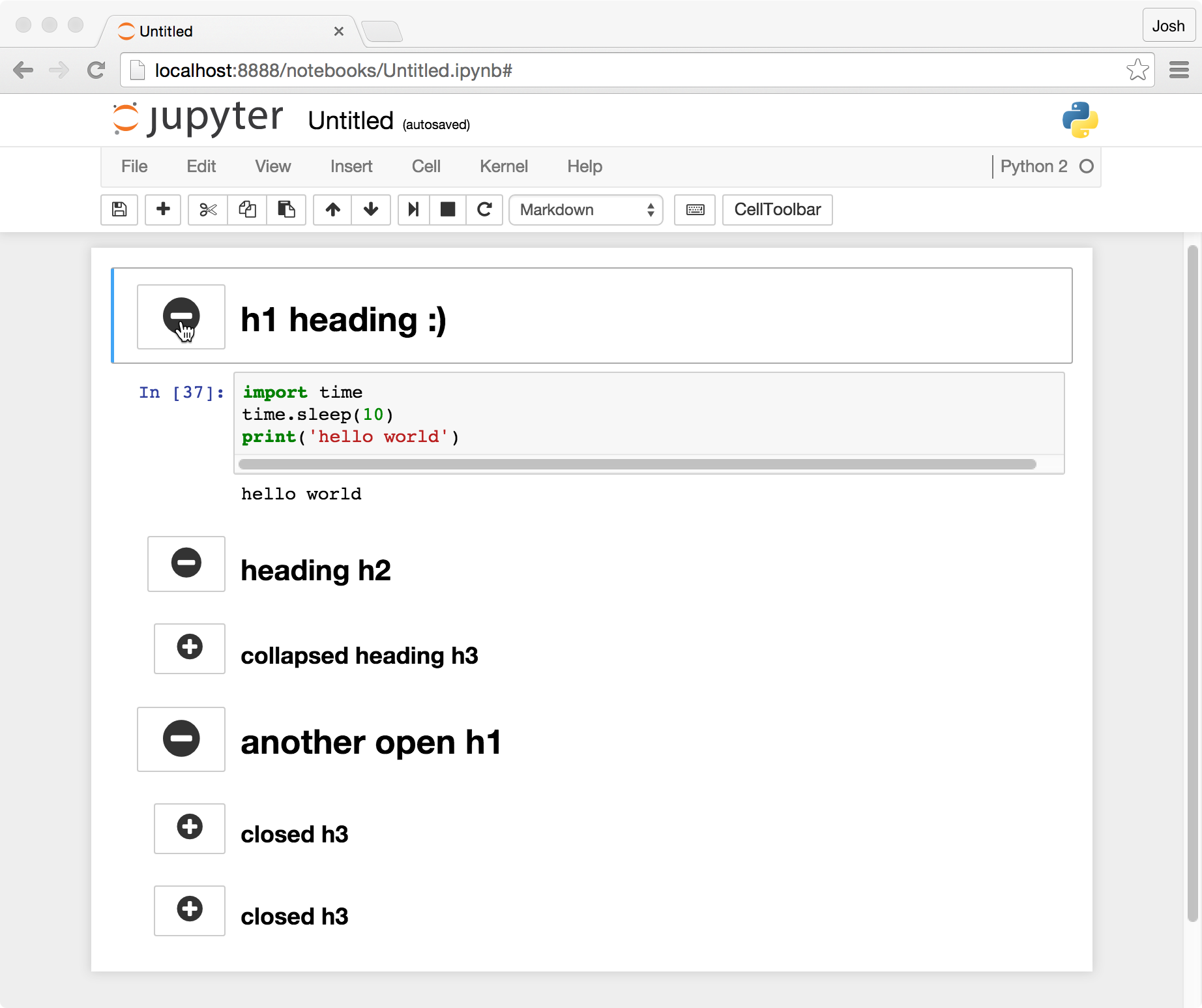
Markdown cell displays text which can be formatted using markdown language. In order to enter a text which should not be treated as code by Notebook server, it must be first converted as markdown cell either from cell menu or by using keyboard shortcut M while in command mode. The In prompt before cell disappears. Jupyter Notebook are the perfect playground for every nerd. The documents are based on JSON, but they follow a versioned schema, and contain ordered lists of input/output cells which can contain code, Markdown text, mathematics, plots and rich media. See what I mean? The markdown cell in Jupyter Notebook can display six levels of heading. For making a heading, start the syntax with # followed by a space and then the text. This will make the heading of level 1 – The biggest. To decrease the size of the heading start incrementing the number of #. Explore and run machine learning code with Kaggle Notebooks Using data from no data sources.
You can write content in regular Markdown files (e.g., files ending in .md).Jupyter Book supports any Markdown syntax that is supported by Jupyter notebooks.Jupyter Notebook Markdown is an extension of a flavour of Markdown calledCommonMark Markdown.It has many elements for standard text processing, though it lacks a lot of features used forpublishing and documentation.
Note
If you'd like a more in-depth overview and guide to CommonMark Markdown, seethe CommonMark Markdown tutorial.
This page describes some basic features of the Jupyter Notebook Markdown, and how toinclude them with your book.

Embedding media¶
Adding images¶
You can reference external media like images from your Markdown file. If you userelative paths, then they will continue to work when the Markdown files are copied over,so long as they point to a file that's inside of the repository.
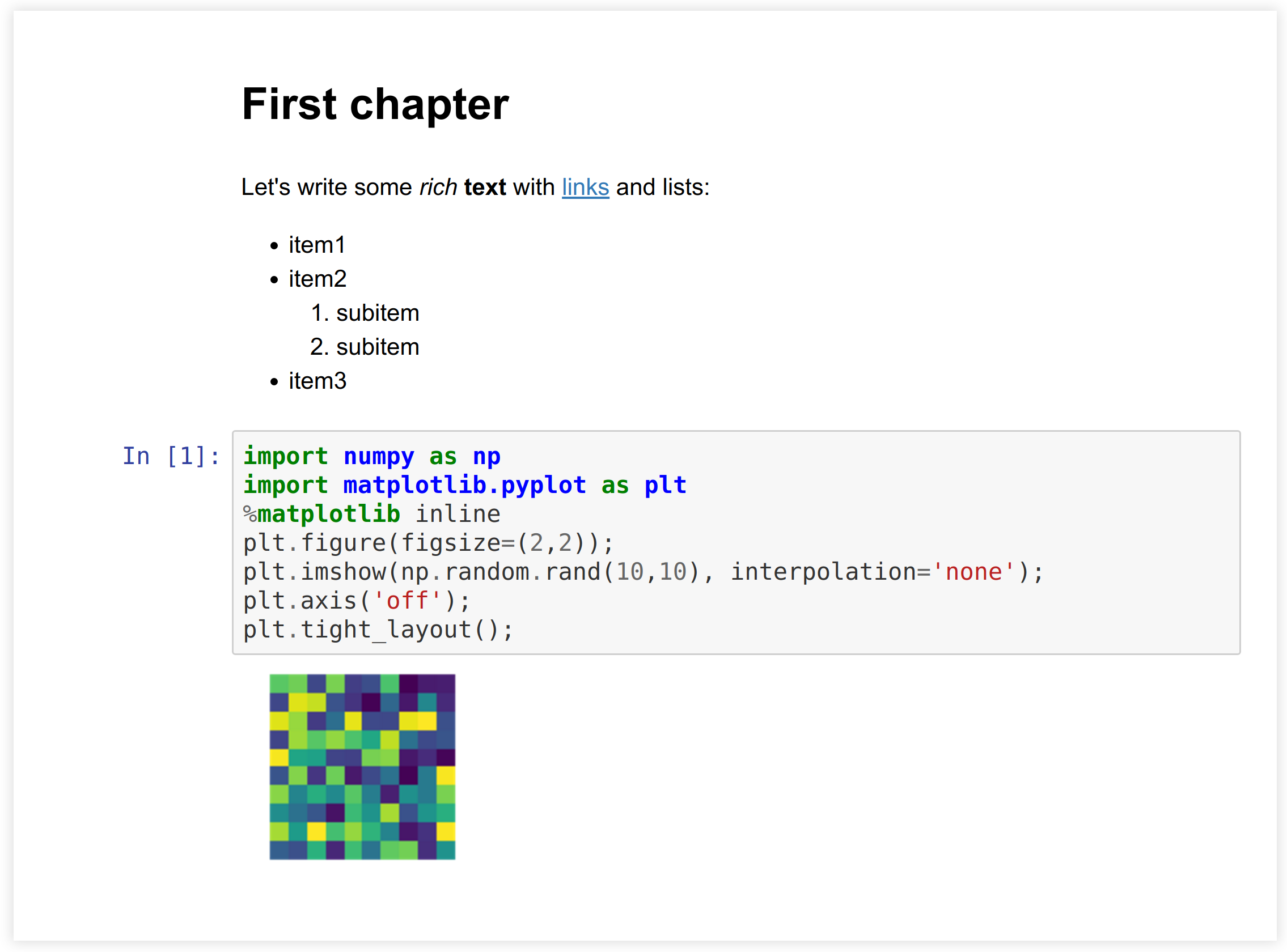
Here's an image relative to the book content root
It was generated with this code:
See also
Images and figures for more information.
Adding movies¶
You can even embed references to movies on the web! For example, here's a little GIF for you!
This will be included in your book when it is built.
Mathematics¶
For HTML outputs, Jupyter Book uses the excellent MathJax library,along with the default Jupyter Notebook configuration, for rendering mathematics from LaTeX-style syntax.
Jupyter Notebook Markdown Font Size
For example, here's a mathematical expression rendered with MathJax:
Block-level mathematics¶
You can include block-level mathematics by wrapping your formulas in $$ characters.For example, the following block:
Results in this output:
Jupiter Notebook Format Markdown Download
You can also include math blocks by using LaTeX-style syntax using begin{align*}.For example, the following block:
Results in:
Markdown cell displays text which can be formatted using markdown language. In order to enter a text which should not be treated as code by Notebook server, it must be first converted as markdown cell either from cell menu or by using keyboard shortcut M while in command mode. The In prompt before cell disappears. Jupyter Notebook are the perfect playground for every nerd. The documents are based on JSON, but they follow a versioned schema, and contain ordered lists of input/output cells which can contain code, Markdown text, mathematics, plots and rich media. See what I mean? The markdown cell in Jupyter Notebook can display six levels of heading. For making a heading, start the syntax with # followed by a space and then the text. This will make the heading of level 1 – The biggest. To decrease the size of the heading start incrementing the number of #. Explore and run machine learning code with Kaggle Notebooks Using data from no data sources.
You can write content in regular Markdown files (e.g., files ending in .md).Jupyter Book supports any Markdown syntax that is supported by Jupyter notebooks.Jupyter Notebook Markdown is an extension of a flavour of Markdown calledCommonMark Markdown.It has many elements for standard text processing, though it lacks a lot of features used forpublishing and documentation.
Note
If you'd like a more in-depth overview and guide to CommonMark Markdown, seethe CommonMark Markdown tutorial.
This page describes some basic features of the Jupyter Notebook Markdown, and how toinclude them with your book.
Embedding media¶
Adding images¶
You can reference external media like images from your Markdown file. If you userelative paths, then they will continue to work when the Markdown files are copied over,so long as they point to a file that's inside of the repository.
Here's an image relative to the book content root
It was generated with this code:
See also
Images and figures for more information.
Adding movies¶
You can even embed references to movies on the web! For example, here's a little GIF for you!
This will be included in your book when it is built.
Mathematics¶
For HTML outputs, Jupyter Book uses the excellent MathJax library,along with the default Jupyter Notebook configuration, for rendering mathematics from LaTeX-style syntax.
Jupyter Notebook Markdown Font Size
For example, here's a mathematical expression rendered with MathJax:
Block-level mathematics¶
You can include block-level mathematics by wrapping your formulas in $$ characters.For example, the following block:
Results in this output:
Jupiter Notebook Format Markdown Download
You can also include math blocks by using LaTeX-style syntax using begin{align*}.For example, the following block:
Results in:
Important
This requires the amsmath MyST extension to be enabled.
Jupyter Notebook Markdown Formatting Cheat Sheet
Extended Markdown with MyST Markdown¶
Jupyter Notebook Format Markdown Cells
In addition to CommonMark Markdown, Jupyter Book also supports a more fully-featured version of Markdown called MyST Markdown.This is a superset of CommonMark that includes syntactic pieces that are useful for publishing computational narratives.For more information about MyST Markdown, see MyST Markdown overview.
